Cloud Integration Built for the Enterprise
We don't just connect systems we architect digital ecosystems that are resilient, flexible, and built for what’s next.
Explore Cloud services
.eJGUafwC.png)






250+
Projects delivered
90%
Clients satisfaction
5+
Years of delivering solutions
1+
No. of countries served
Services we provide
Geographic Information System
We offer custom GIS development services, delivering powerful solutions for geospatial data capture, visualization, analysis, and integration. Our expertise spans web-based GIS applications, location intelligence tools, and enterprise-grade mapping systems tailored to meet diverse business needs.
- Implementation & Management
- Data Management – Analysis & Visualizations
- Engineering CAD Services
- Image Services

Services we provide
We offer custom GIS development services, delivering powerful solutions for geospatial data capture, visualization, analysis, and integration. Our expertise spans web-based GIS applications, location intelligence tools, and enterprise-grade mapping systems tailored to meet diverse business needs.
- Implementation & Management
- Data Management – Analysis & Visualizations
- Engineering CAD Services
- Image Services
Our products:



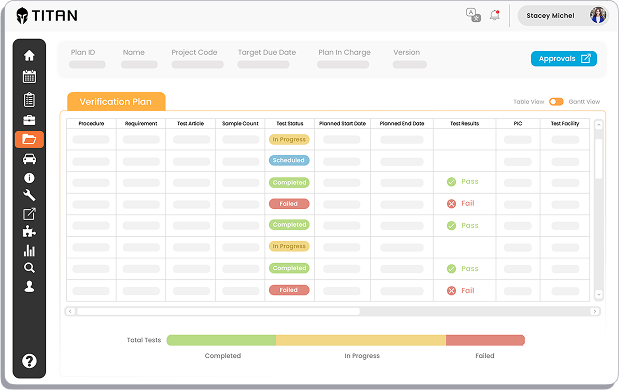
TITAN is an all-in-one Test Lifecycle Management solution.
TITAN streamlines test planning, scheduling, and resource management, promoting collaboration and simplifying data. It offers features like test unit, equipment and lab management, data, incident, and work order management. TITAN optimizes the testing process, saving time and money.

NetGraph is a platform designed to streamline the digitization/conversion process for various network data types, including Telecom, FOW, and Utilities such as Electrical, Gas, Water, Sewage, and cadastral.
Features
Efficient Digitization
Streamline the process of converting network data into digital formats.
Versatile Support
Handles diverse data types including Telecom, FOW, and Utilities such as Electrical, Gas, Water, Sewage, and cadastral.
Georeferenced Background
Utilizes georeferenced raster images or scanned maps as visual references.
Simplified Workflow
Offers a user-friendly interface for seamless navigation and operation.
Have questions about our products or services?
Contact Us – we’re here to help
Get in touch today! 

